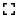Federal Reserve Economic Data: Your trusted data source since 1991
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
NOTES
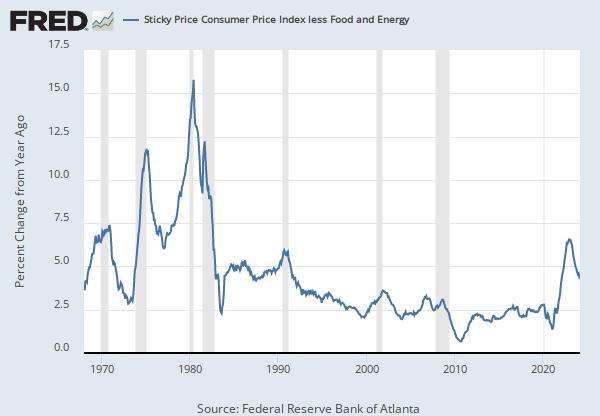
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Consumer Price Index
Units: Index 1982-1984=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items (CPIAUCSL) is a price index of a basket of goods and services paid by urban consumers. Percent changes in the price index measure the inflation rate between any two time periods. The most common inflation metric is the percent change from one year ago. It can also represent the buying habits of urban consumers. This particular index includes roughly 88 percent of the total population, accounting for wage earners, clerical workers, technical workers, self-employed, short-term workers, unemployed, retirees, and those not in the labor force.
The CPIs are based on prices for food, clothing, shelter, and fuels; transportation fares; service fees (e.g., water and sewer service); and sales taxes. Prices are collected monthly from about 4,000 housing units and approximately 26,000 retail establishments across 87 urban areas. To calculate the index, price changes are averaged with weights representing their importance in the spending of the particular group. The index measures price changes (as a percent change) from a predetermined reference date. In addition to the original unadjusted index distributed, the Bureau of Labor Statistics also releases a seasonally adjusted index. The unadjusted series reflects all factors that may influence a change in prices. However, it can be very useful to look at the seasonally adjusted CPI, which removes the effects of seasonal changes, such as weather, school year, production cycles, and holidays.
The CPI can be used to recognize periods of inflation and deflation. Significant increases in the CPI within a short time frame might indicate a period of inflation, and significant decreases in CPI within a short time frame might indicate a period of deflation. However, because the CPI includes volatile food and oil prices, it might not be a reliable measure of inflationary and deflationary periods. For a more accurate detection, the core CPI (CPILFESL) is often used. When using the CPI, please note that it is not applicable to all consumers and should not be used to determine relative living costs. Additionally, the CPI is a statistical measure vulnerable to sampling error since it is based on a sample of prices and not the complete average.
For more information on the consumer price indexes, see:
Bureau of Economic Analysis. "CPI Detailed Report." 2013.
Handbook of Methods
Understanding the CPI: Frequently Asked Questions
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items in U.S. City Average [CPIAUCSL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CPIAUCSL, April 25, 2024.
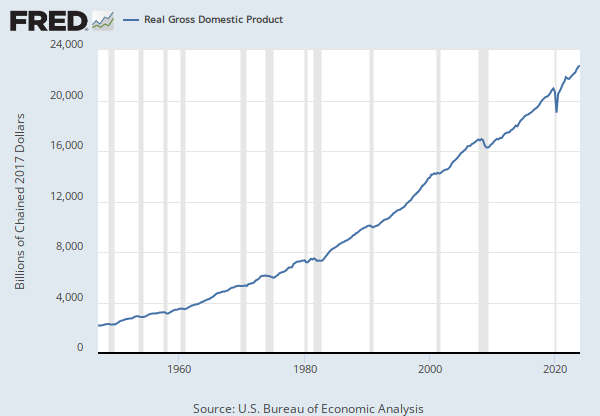
Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
Release: Personal Income and Outlays
Units: Billions of Dollars, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
BEA Account Code: DPCERC
A Guide to the National Income and Product Accounts of the United States (NIPA).
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Personal Consumption Expenditures [PCE], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PCE, April 25, 2024.
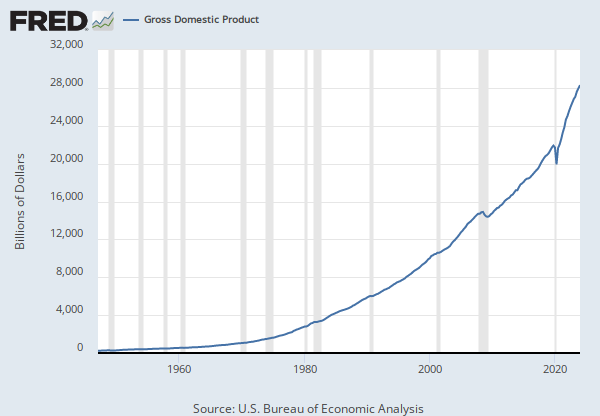
Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
Release: Personal Income and Outlays
Units: Billions of Chained 2017 Dollars, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
BEA Account Code: A067RX
AGuide to the National Income and Product Accounts of the United States (NIPA)
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Real Disposable Personal Income [DSPIC96], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/DSPIC96, April 25, 2024.
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
Release: Money Velocity
Units: Ratio, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Quarterly
Notes:
Calculated as the ratio of quarterly nominal GDP (GDP) to the quarterly average of M1 money stock (M1SL)
The velocity of money is the frequency at which one unit of currency is used to purchase domestically- produced goods and services within a given time period. In other words, it is the number of times one dollar is spent to buy goods and services per unit of time. If the velocity of money is increasing, then more transactions are occurring between individuals in an economy.
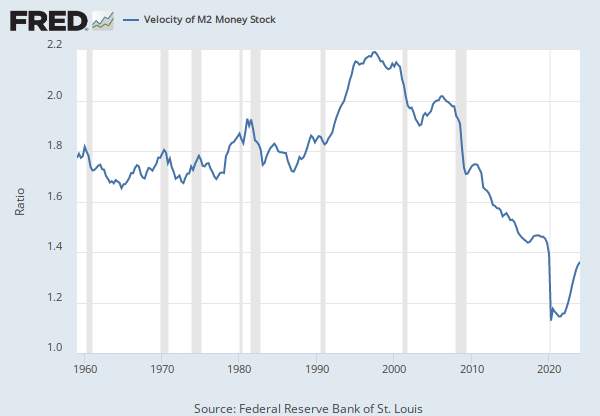
The frequency of currency exchange can be used to determine the velocity of a given component of the money supply, providing some insight into whether consumers and businesses are saving or spending their money. There are several components of the money supply,: M1, M2, and MZM (M3 is no longer tracked by the Federal Reserve); these components are arranged on a spectrum of narrowest to broadest. Consider M1, the narrowest component. M1 is the money supply of currency in circulation (notes and coins, demand deposits, and other liquid deposits). A decreasing velocity of M1 might indicate fewer short- term consumption transactions are taking place. We can think of shorter- term transactions as consumption we might make on an everyday basis.
Beginning May 2020, M1 consists of (1) currency outside the U.S. Treasury, Federal Reserve Banks, and the vaults of depository institutions; (2) demand deposits at commercial banks (excluding those amounts held by depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign banks and official institutions) less cash items in the process of collection and Federal Reserve float; and (3) other liquid deposits, consisting of OCDs and savings deposits (including money market deposit accounts). Seasonally adjusted M1 is constructed by summing currency, demand deposits, and OCDs (before May 2020) or other liquid deposits (beginning May 2020), each seasonally adjusted separately. For more information on the H.6 release changes and the regulatory amendment that led to the creation of the other liquid deposits component and its inclusion in the M1 monetary aggregate, see the H.6 announcements and Technical Q&As posted on December 17, 2020.
The broader M2 component includes M1 in addition to saving deposits, certificates of deposit (less than $100,000), and money market deposits for individuals. Comparing the velocities of M1 and M2 provides some insight into how quickly the economy is spending and how quickly it is saving.
MZM (money with zero maturity) is the broadest component and consists of the supply of financial assets redeemable at par on demand: notes and coins in circulation, traveler’s checks (non-bank issuers), demand deposits, other checkable deposits, savings deposits, and all money market funds. The velocity of MZM helps determine how often financial assets are switching hands within the economy.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Velocity of M1 Money Stock [M1V], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/M1V, April 25, 2024.
Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
Release: Personal Income and Outlays
Units: Percent, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
BEA Account Code: A072RC
Personal saving as a percentage of disposable personal income (DPI), frequently referred to as "the personal saving rate," is calculated as the ratio of personal saving to DPI.
Personal saving is equal to personal income less personal outlays and personal taxes; it may generally be viewed as the portion of personal income that is used either to provide funds to capital markets or to invest in real assets such as residences.(https://www.bea.gov/national/pdf/all-chapters.pdf)
A Guide to the National Income and Product Accounts of the United States (NIPA).
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Personal Saving Rate [PSAVERT], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PSAVERT, April 25, 2024.
RELEASE TABLES
RELATED DATA AND CONTENT
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items in U.S. City Average
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Semiannual, Not Seasonally AdjustedPersonal Consumption Expenditures
Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Quarterly, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate Index 2017=100, Quarterly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars, Quarterly, Not Seasonally AdjustedReal Disposable Personal Income
Quarterly, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate Percent Change from Preceding Period, Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change from Preceding Period, Quarterly, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate Percent Change from Quarter One Year Ago, Quarterly, Seasonally Adjusted