Federal Reserve Economic Data
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
Source: University of Groningen
Source: University of California, Davis
Release: Penn World Table 10.01
Units: Index 2017=1, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Annual
Notes:
Source ID: rtfpna
When using these data in your research, please make the following reference: Feenstra, Robert C., Robert Inklaar and Marcel P. Timmer (2015), "The Next Generation of the Penn World Table" American Economic Review, 105(10), 3150-3182, available for download at www.ggdc.net/pwt
For more information, see http://www.rug.nl/research/ggdc/data/pwt/.
Suggested Citation:
University of Groningen and University of California, Davis, Total Factor Productivity at Constant National Prices for United States [RTFPNAUSA632NRUG], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/RTFPNAUSA632NRUG, .
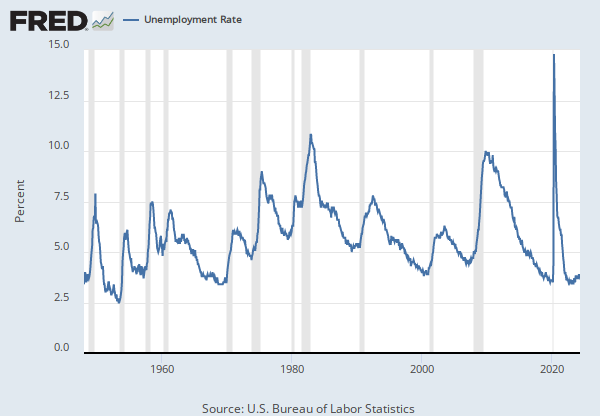
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Employment Situation
Units: Percent, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The series comes from the 'Current Population Survey (Household Survey)'
The source code is: LNS11300000
The Labor Force Participation Rate is defined by the Current Population Survey (CPS) as “the number of people in the labor force as a percentage of the civilian noninstitutional population […] the participation rate is the percentage of the population that is either working or actively looking for work.”
The Labor Force Participation Rate is collected in the CPS and published by the BLS. It is provided on a monthly basis, so this data is used in part by macroeconomists as an initial economic indicator of current labor market trends. The labor force participation rate helps government agencies, financial markets, and researchers gauge the overall health of the economy.
Note that long-run changes in labor force participation may reflect secular economic trends that are unrelated to the overall health of the economy. For instance, demographic changes such as the aging of population can lead to a secular increase of exits from the labor force, shrinking the labor force and decreasing the labor force participation rate.
For more information, see:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, CES Overview
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Concepts and Definitions (CPS)
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Labor Force Participation Rate [CIVPART], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CIVPART, .
Release Tables
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Related Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.