Federal Reserve Economic Data
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
Release: Money Velocity
Units: Ratio, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Quarterly
Notes:
This series has been discontinued and will no longer be updated. The institutional money market funds component (IMFSL) used to calculate MZM has been discontinued by the Board of Governors and is no longer available in the H.6 statistical release, Money Stock Measures. For further information about the changes to the H.6 statistical release, please see the announcements provided by the source.
Calculated as the ratio of quarterly nominal GDP (GDP) to the quarterly average of MZM money stock (MZMSL).
The velocity of money is the frequency at which one unit of currency is used to purchase domestically- produced goods and services within a given time period. In other words, it is the number of times one dollar is spent to buy goods and services per unit of time. If the velocity of money is increasing, then more transactions are occurring between individuals in an economy.
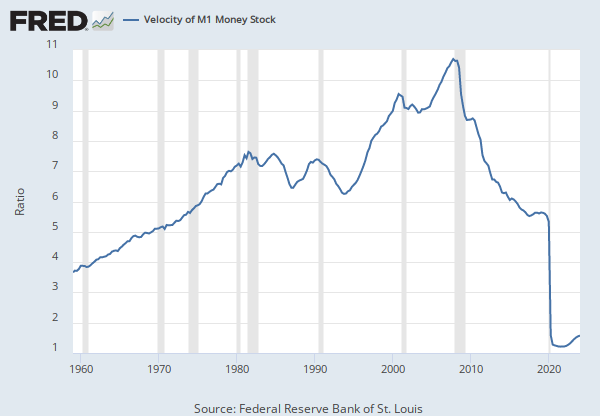
The frequency of currency exchange can be used to determine the velocity of a given component of the money supply, providing some insight into whether consumers and businesses are saving or spending their money. There are several components of the money supply,: M1, M2, and MZM (M3 is no longer tracked by the Federal Reserve); these components are arranged on a spectrum of narrowest to broadest. Consider M1, the narrowest component. M1 is the money supply of currency in circulation (notes and coins, traveler’s checks [non-bank issuers], demand deposits, and checkable deposits). A decreasing velocity of M1 might indicate fewer short- term consumption transactions are taking place. We can think of shorter- term transactions as consumption we might make on an everyday basis.
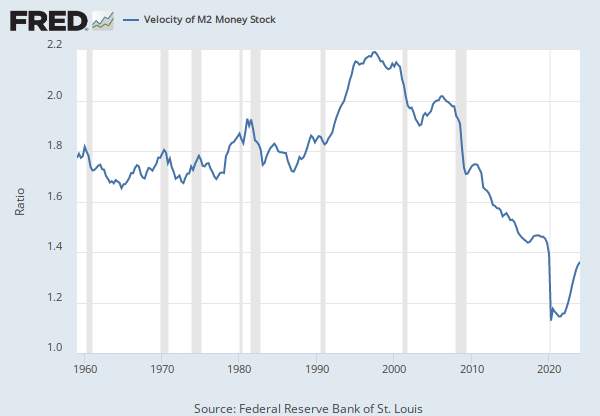
The broader M2 component includes M1 in addition to saving deposits, certificates of deposit (less than $100,000), and money market deposits for individuals. Comparing the velocities of M1 and M2 provides some insight into how quickly the economy is spending and how quickly it is saving.
MZM (money with zero maturity) is the broadest component and consists of the supply of financial assets redeemable at par on demand: notes and coins in circulation, traveler’s checks (non-bank issuers), demand deposits, other checkable deposits, savings deposits, and all money market funds. The velocity of MZM helps determine how often financial assets are switching hands within the economy.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Velocity of MZM Money Stock (DISCONTINUED) [MZMV], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/MZMV, .
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: H.15 Selected Interest Rates
Units: Percent, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Daily
Notes:
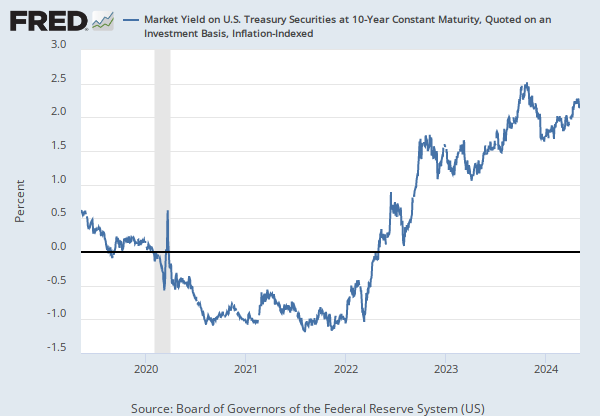
For further information regarding treasury constant maturity data, please refer to the H.15 Statistical Release notes and Treasury Yield Curve Methodology.
For questions on the data, please contact the data source. For questions on FRED functionality, please contact us here.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Market Yield on U.S. Treasury Securities at 10-Year Constant Maturity, Quoted on an Investment Basis [DGS10], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/DGS10, .
Release Tables
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Related Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.