Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: H.4.1 Factors Affecting Reserve Balances
Units: Millions of U.S. Dollars, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Weekly, As of Wednesday
Notes:
For questions on the data, please contact the data source. For questions on FRED functionality, please contact us here.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Assets: Other: Repurchase Agreements: Wednesday Level [WORAL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/WORAL, .
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: H.4.1 Factors Affecting Reserve Balances
Units: Millions of U.S. Dollars, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Weekly, As of Wednesday
Notes:
For questions on the data, please contact the data source. For questions on FRED functionality, please contact us here.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Liabilities and Capital: Liabilities: Reverse Repurchase Agreements: Wednesday Level [WLRRAL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/WLRRAL, .
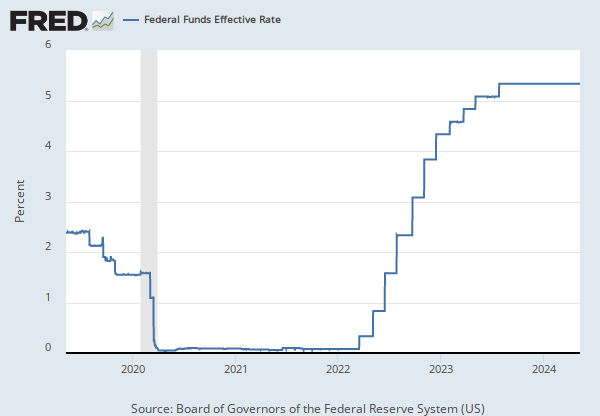
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Release: Federal Funds Data
Units: Percent, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Daily
Notes:
For additional historical federal funds rate data, please see Daily Federal Funds Rate from 1928-1954.
The federal funds market consists of domestic unsecured borrowings in U.S. dollars by depository institutions from other depository institutions and certain other entities, primarily government-sponsored enterprises.
The effective federal funds rate (EFFR) is calculated as a volume-weighted median of overnight federal funds transactions reported in the FR 2420 Report of Selected Money Market Rates.
For more information, visit the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Effective Federal Funds Rate [EFFR], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/EFFR, .
Release Tables
- Table 1. Factors Affecting Reserve Balances of Depository Institutions: Wednesday Level
- Table 2. Maturity Distribution of Securities, Loans, and Selected Other Assets and Liabilities
- Table 5. Consolidated Statement of Condition of All Federal Reserve Banks
- Table 6. Statement of Condition of Each Federal Reserve Bank
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Related Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.