Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
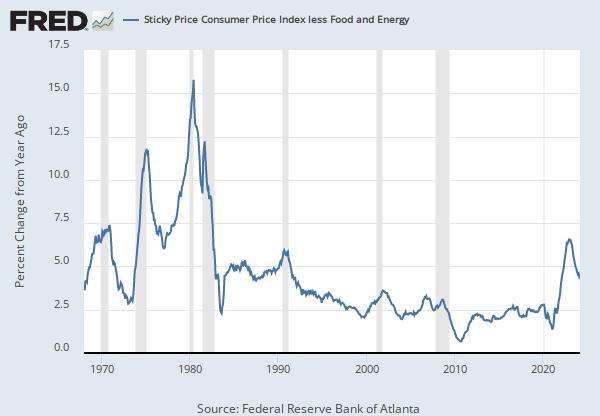
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta
Release: Sticky Price CPI
Units: Percent Change from Year Ago, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The Sticky Price Consumer Price Index (CPI) is calculated from a subset of goods and services included in the CPI that change price relatively infrequently. Because these goods and services change price relatively infrequently, they are thought to incorporate expectations about future inflation to a greater degree than prices that change on a more frequent basis. One possible explanation for sticky prices could be the costs firms incur when changing price.
To obtain more information about this release see: Michael F. Bryan, and Brent H. Meyer. “Are Some Prices in the CPI More Forward Looking Than Others? We Think So.” Economic Commentary (Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland) (May 19, 2010): 1–6. https://doi.org/10.26509/frbc-ec-201002.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, Sticky Price Consumer Price Index less Food and Energy [CORESTICKM159SFRBATL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CORESTICKM159SFRBATL, .
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland
Release: Current Median CPI
Units: Percent Change at Annual Rate, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
Median Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure of core inflation calculated the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland and the Ohio State University. Median CPI was created as a different way to get a 'Core CPI' measure, or a better measure of underlying inflation trends. To calculate the Median CPI, the Cleveland Fed analyzes the median price change of the goods and services published by the BLS. The median price change is the price change that's right in the middle of the long list of all of the price changes. This series excludes 49.5% of the CPI components with the highest and lowest one-month price changes from each tail of the price-change distribution resulting in a Median CPI Inflation Estimate.
According to research from the Cleveland Fed, the Median CPI provides a better signal of the inflation trend than either the all-items CPI or the CPI excluding food and energy. According to newer research done at the Cleveland Fed, the Median CPI is even better at PCE inflation in the near and longer term than the core PCE.
For further information, visit The Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, Median Consumer Price Index [MEDCPIM158SFRBCLE], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/MEDCPIM158SFRBCLE, .
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Consumer Price Index
Units: Index 1982-1984=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items (CPIAUCSL) is a price index of a basket of goods and services paid by urban consumers. Percent changes in the price index measure the inflation rate between any two time periods. The most common inflation metric is the percent change from one year ago. It can also represent the buying habits of urban consumers. This particular index includes roughly 88 percent of the total population, accounting for wage earners, clerical workers, technical workers, self-employed, short-term workers, unemployed, retirees, and those not in the labor force.
The CPIs are based on prices for food, clothing, shelter, and fuels; transportation fares; service fees (e.g., water and sewer service); and sales taxes. Prices are collected monthly from about 4,000 housing units and approximately 26,000 retail establishments across 87 urban areas. To calculate the index, price changes are averaged with weights representing their importance in the spending of the particular group. The index measures price changes (as a percent change) from a predetermined reference date. In addition to the original unadjusted index distributed, the Bureau of Labor Statistics also releases a seasonally adjusted index. The unadjusted series reflects all factors that may influence a change in prices. However, it can be very useful to look at the seasonally adjusted CPI, which removes the effects of seasonal changes, such as weather, school year, production cycles, and holidays.
The CPI can be used to recognize periods of inflation and deflation. Significant increases in the CPI within a short time frame might indicate a period of inflation, and significant decreases in CPI within a short time frame might indicate a period of deflation. However, because the CPI includes volatile food and oil prices, it might not be a reliable measure of inflationary and deflationary periods. For a more accurate detection, the core CPI (CPILFESL) is often used. When using the CPI, please note that it is not applicable to all consumers and should not be used to determine relative living costs. Additionally, the CPI is a statistical measure vulnerable to sampling error since it is based on a sample of prices and not the complete average.
For more information on the CPI, see the Handbook of Methods, the release notes and announcements, and the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs).
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items in U.S. City Average [CPIAUCSL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CPIAUCSL, .
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Consumer Price Index
Units: Index 1982-1984=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The "Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food & Energy" is an aggregate of prices paid by urban consumers for a typical basket of goods, excluding food and energy. This measurement, known as "Core CPI," is widely used by economists because food and energy have very volatile prices. The Bureau of Labor Statistics defines and measures the official CPI, and more information can be found in the FAQ or in this article.
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food and Energy in U.S. City Average [CPILFESL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CPILFESL, .
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Consumer Price Index
Units: Index 1982-1984=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: Shelter in U.S. City Average [CUSR0000SAH1], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CUSR0000SAH1, .
Release Tables
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Sticky Price Consumer Price Index less Food and Energy
3-Month Annualized Percent Change, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change at Annual Rate, Monthly, Seasonally AdjustedMedian Consumer Price Index
Index Dec 1982=100, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change from Year Ago, Monthly, Seasonally AdjustedConsumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items in U.S. City Average
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Semiannual, Not Seasonally AdjustedConsumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food and Energy in U.S. City Average
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Semiannual, Not Seasonally AdjustedConsumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: Shelter in U.S. City Average
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Semiannual, Not Seasonally AdjustedRelated Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.