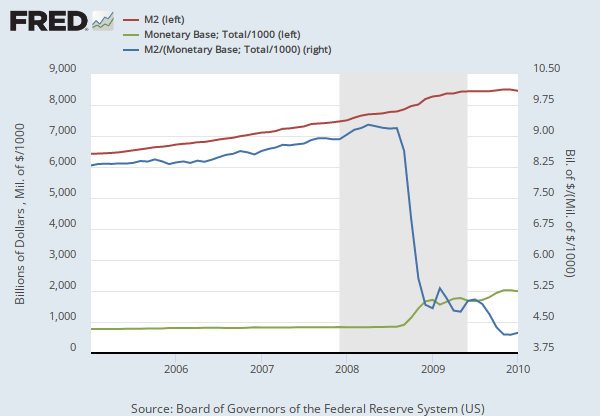
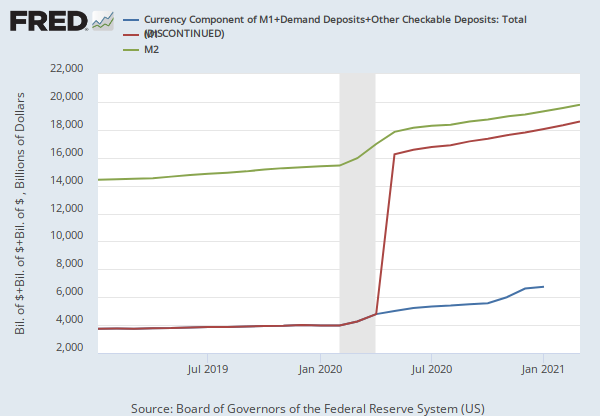
Federal Reserve Economic Data
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
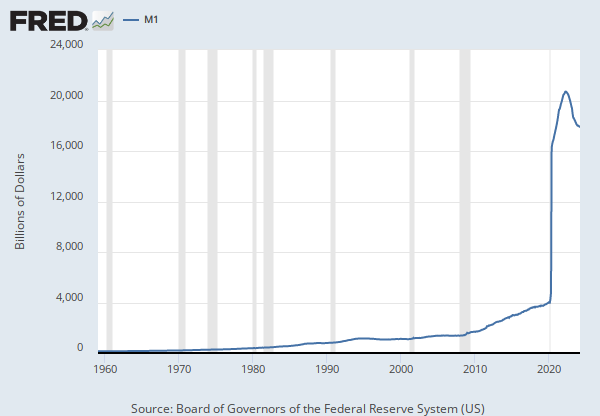
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: H.6 Money Stock Measures
Units: Billions of Dollars, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
Before May 2020, M2 consists of M1 plus (1) savings deposits (including money market deposit accounts); (2) small-denomination time deposits (time deposits in amounts of less than $100,000) less individual retirement account (IRA) and Keogh balances at depository institutions; and (3) balances in retail money market funds (MMFs) less IRA and Keogh balances at MMFs.
Beginning May 2020, M2 consists of M1 plus (1) small-denomination time deposits (time deposits in amounts of less than $100,000) less IRA and Keogh balances at depository institutions; and (2) balances in retail MMFs less IRA and Keogh balances at MMFs. Seasonally adjusted M2 is constructed by summing savings deposits (before May 2020), small-denomination time deposits, and retail MMFs, each seasonally adjusted separately, and adding this result to seasonally adjusted M1.
For more information on the H.6 release changes and the regulatory amendment that led to the creation of the other liquid deposits component and its inclusion in the M1 monetary aggregate, see the H.6 announcements and Technical Q&As posted on December 17, 2020.
For questions on the data, please contact the data source. For questions on FRED functionality, please contact us here.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), M2 [M2SL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/M2SL, .
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta
Release: Sticky Price CPI
Units: Percent Change from Year Ago, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The Sticky Price Consumer Price Index (CPI) is calculated from a subset of goods and services included in the CPI that change price relatively infrequently. Because these goods and services change price relatively infrequently, they are thought to incorporate expectations about future inflation to a greater degree than prices that change on a more frequent basis. One possible explanation for sticky prices could be the costs firms incur when changing price.
To obtain more information about this release see: Michael F. Bryan, and Brent H. Meyer. “Are Some Prices in the CPI More Forward Looking Than Others? We Think So.” Economic Commentary (Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland) (May 19, 2010): 1–6. https://doi.org/10.26509/frbc-ec-201002.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, Sticky Price Consumer Price Index less Food and Energy [CORESTICKM159SFRBATL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CORESTICKM159SFRBATL, .
Release Tables
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
M2
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Weekly, Not Seasonally AdjustedSticky Price Consumer Price Index less Food and Energy
3-Month Annualized Percent Change, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change at Annual Rate, Monthly, Seasonally AdjustedRelated Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.