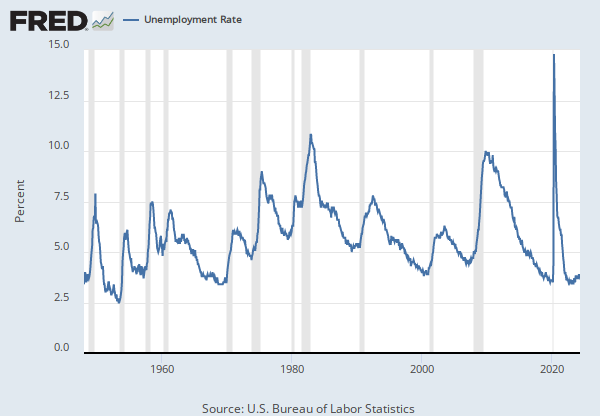
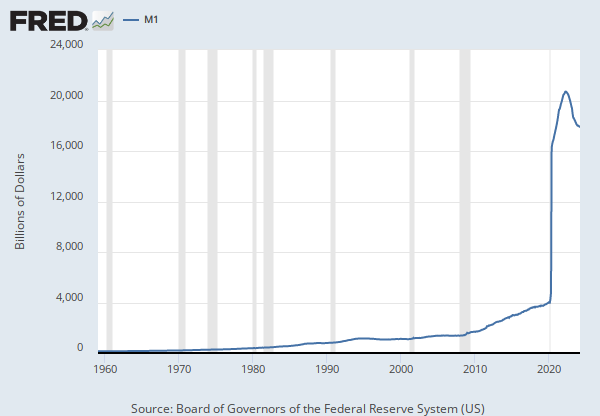
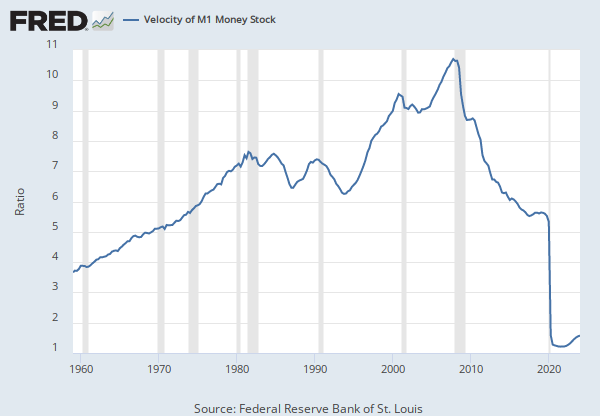
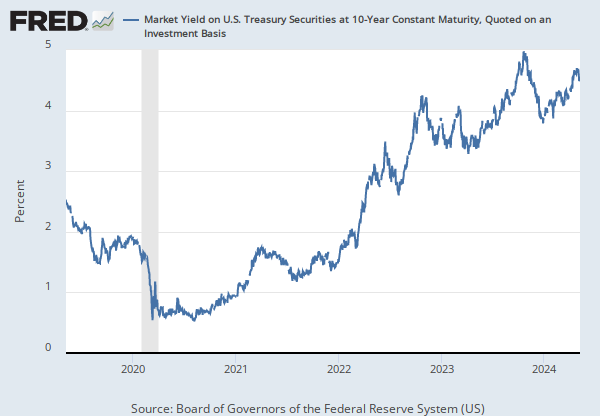
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: H.6 Money Stock Measures
Units: Billions of Dollars, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Weekly, Ending Monday
Notes:
This weekly series is discontinued and will no longer be updated. The non-seasonally adjusted version of this weekly series is WM1NS, and the seasonally adjusted monthly series is M1SL.
Starting on February 23, 2021, the H.6 statistical release is now published at a monthly frequency and contains only monthly average data needed to construct the monetary aggregates. Weekly average, non-seasonally adjusted data will continue to be made available, while weekly average, seasonally adjusted data will no longer be provided. For further information about the changes to the H.6 statistical release, see the announcements provided by the source.
Before May 2020, M1 consists of (1) currency outside the U.S. Treasury, Federal Reserve Banks, and the vaults of depository institutions; (2) demand deposits at commercial banks (excluding those amounts held by depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign banks and official institutions) less cash items in the process of collection and Federal Reserve float; and (3) other checkable deposits (OCDs), consisting of negotiable order of withdrawal, or NOW, and automatic transfer service, or ATS, accounts at depository institutions, share draft accounts at credit unions, and demand deposits at thrift institutions.
Beginning May 2020, M1 consists of (1) currency outside the U.S. Treasury, Federal Reserve Banks, and the vaults of depository institutions; (2) demand deposits at commercial banks (excluding those amounts held by depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign banks and official institutions) less cash items in the process of collection and Federal Reserve float; and (3) other liquid deposits, consisting of OCDs and savings deposits (including money market deposit accounts). Seasonally adjusted M1 is constructed by summing currency, demand deposits, and OCDs (before May 2020) or other liquid deposits (beginning May 2020), each seasonally adjusted separately.
For more information on the H.6 release changes and the regulatory amendment that led to the creation of the other liquid deposits component and its inclusion in the M1 monetary aggregate, see the H.6 announcements and Technical Q&As posted on December 17, 2020.
For questions on the data, please contact the data source. For questions on FRED functionality, please contact us here.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), M1 (DISCONTINUED) [M1], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/M1, .
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: Z.1 Financial Accounts of the United States
Units: Millions of U.S. Dollars, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate
Frequency: Quarterly, End of Period
Notes:
For more information about the Flow of Funds tables, see the Financial Accounts Guide.
With each quarterly release, the source may make major data and structural revisions to the series and tables. These changes are available in the Release Highlights.
In the Financial Accounts, the source identifies each series by a string of patterned letters and numbers. For a detailed description, including how this series is constructed, see the series analyzer provided by the source.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Nonfinancial Corporate Business; Debt Securities and Loans; Liability, Level [BCNSDODNS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/BCNSDODNS, .
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: H.15 Selected Interest Rates
Units: Percent, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
Averages of daily figures.
For additional historical federal funds rate data, please see Daily Federal Funds Rate from 1928-1954.
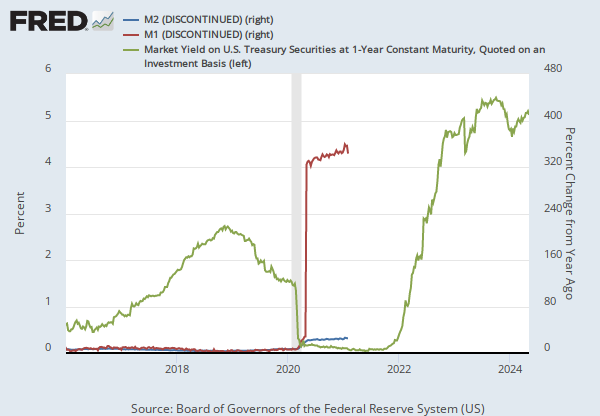
The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions trade federal funds (balances held at Federal Reserve Banks) with each other overnight. When a depository institution has surplus balances in its reserve account, it lends to other banks in need of larger balances. In simpler terms, a bank with excess cash, which is often referred to as liquidity, will lend to another bank that needs to quickly raise liquidity. (1) The rate that the borrowing institution pays to the lending institution is determined between the two banks; the weighted average rate for all of these types of negotiations is called the effective federal funds rate.(2) The effective federal funds rate is essentially determined by the market but is influenced by the Federal Reserve as it uses the Interest on Reserve Balances rate to steer the federal funds rate toward the target range.(2)
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets eight times a year to determine the federal funds target range. The Fed's primary tool for influencing the federal funds rate is the interest the Fed pays on the funds that banks hold as reserve balances at their Federal Reserve Bank, which is the Interest on Reserves Balances (IORB) rate. Because banks are unlikely to lend funds in the federal funds market for less than they get paid in their reserve balance account at the Federal Reserve, the Interest on Reserve Balances (IORB) is an effective tool for guiding the federal funds rate. (3) Whether the Federal Reserve raises or lowers the target range for the federal funds rate depends on the state of the economy. If the FOMC believes the economy is growing too fast and inflation pressures are inconsistent with the dual mandate of the Federal Reserve, the Committee may temper economic activity by raising the target range for federal funds rate, and increasing the IORB rate to steer the federal funds rate into the target range. In the opposing scenario, the FOMC may spur greater economic activity by lowering the target range for federal funds rate, and decreasing the IORB rate to steer the federal funds rate into the target range. (3) Therefore, the FOMC must observe the current state of the economy to determine the best course of monetary policy that will maximize economic growth while adhering to the dual mandate set forth by Congress. In making its monetary policy decisions, the FOMC considers a wealth of economic data, such as: trends in prices and wages, employment, consumer spending and income, business investments, and foreign exchange markets.
The federal funds rate is the central interest rate in the U.S. financial market. It influences other interest rates such as the prime rate, which is the rate banks charge their customers with higher credit ratings. Additionally, the federal funds rate indirectly influences longer- term interest rates such as mortgages, loans, and savings, all of which are very important to consumer wealth and confidence.(2)
References
(1) Federal Reserve Bank of New York. "Federal funds." Fedpoints, August 2007.
(2) Monetary Policy, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
(3) The Fed Explained, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
For further information, see The Fed's New Monetary Policy Tools, Page One Economics, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
For questions on the data, please contact the data source. For questions on FRED functionality, please contact us here.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Federal Funds Effective Rate [FEDFUNDS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FEDFUNDS, .
Release Tables
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Nonfinancial Corporate Business; Debt Securities and Loans; Liability, Level
Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Annual, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate Quarterly, Not Seasonally AdjustedFederal Funds Effective Rate
Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Biweekly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Daily, Not Seasonally Adjusted Daily, Not Seasonally Adjusted Weekly, Not Seasonally AdjustedRelated Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.