Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
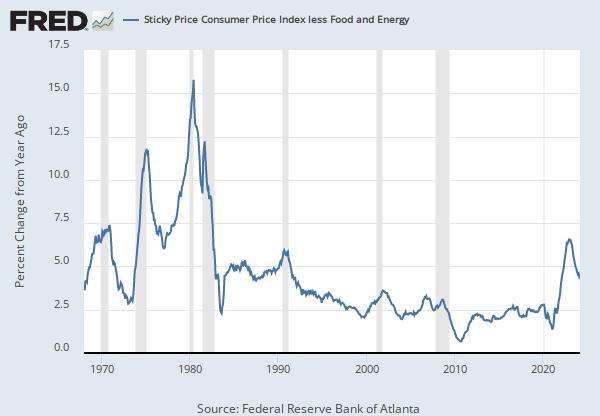
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta
Release: Sticky Price CPI
Units: Percent Change from Year Ago, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The Sticky Price Consumer Price Index (CPI) is calculated from a subset of goods and services included in the CPI that change price relatively infrequently. Because these goods and services change price relatively infrequently, they are thought to incorporate expectations about future inflation to a greater degree than prices that change on a more frequent basis. One possible explanation for sticky prices could be the costs firms incur when changing price.
To obtain more information about this release see: Michael F. Bryan, and Brent H. Meyer. “Are Some Prices in the CPI More Forward Looking Than Others? We Think So.” Economic Commentary (Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland) (May 19, 2010): 1–6. https://doi.org/10.26509/frbc-ec-201002.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, Sticky Price Consumer Price Index [STICKCPIM159SFRBATL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/STICKCPIM159SFRBATL, .
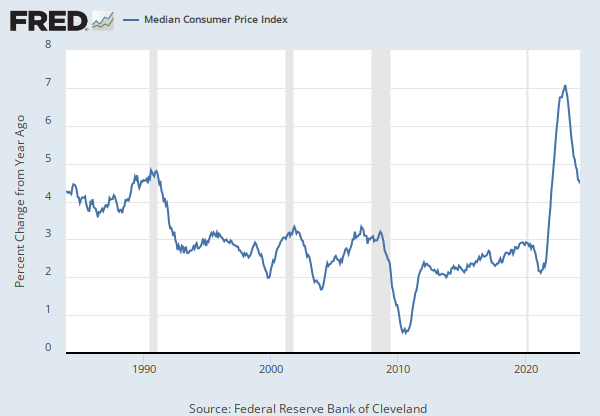
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Consumer Price Index
Units: Index 1982-1984=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The "Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food & Energy" is an aggregate of prices paid by urban consumers for a typical basket of goods, excluding food and energy. This measurement, known as "Core CPI," is widely used by economists because food and energy have very volatile prices. The Bureau of Labor Statistics defines and measures the official CPI, and more information can be found in the FAQ or in this article.
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food and Energy in U.S. City Average [CPILFESL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CPILFESL, .
Release Tables
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Sticky Price Consumer Price Index
3-Month Annualized Percent Change, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change at Annual Rate, Monthly, Seasonally AdjustedConsumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food and Energy in U.S. City Average
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Semiannual, Not Seasonally AdjustedRelated Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.