Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Consumer Price Index
Units: Index 1982-1984=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
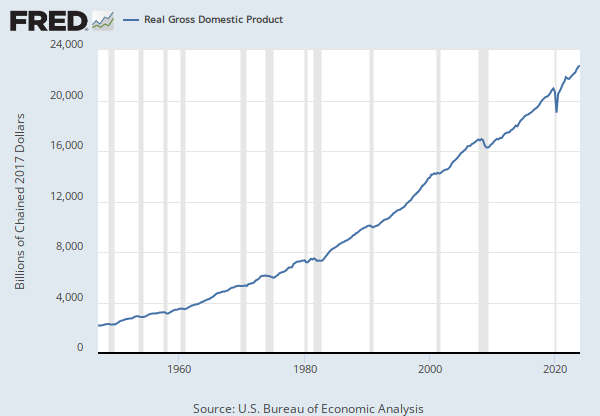
The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items (CPIAUCSL) is a price index of a basket of goods and services paid by urban consumers. Percent changes in the price index measure the inflation rate between any two time periods. The most common inflation metric is the percent change from one year ago. It can also represent the buying habits of urban consumers. This particular index includes roughly 88 percent of the total population, accounting for wage earners, clerical workers, technical workers, self-employed, short-term workers, unemployed, retirees, and those not in the labor force.
The CPIs are based on prices for food, clothing, shelter, and fuels; transportation fares; service fees (e.g., water and sewer service); and sales taxes. Prices are collected monthly from about 4,000 housing units and approximately 26,000 retail establishments across 87 urban areas. To calculate the index, price changes are averaged with weights representing their importance in the spending of the particular group. The index measures price changes (as a percent change) from a predetermined reference date. In addition to the original unadjusted index distributed, the Bureau of Labor Statistics also releases a seasonally adjusted index. The unadjusted series reflects all factors that may influence a change in prices. However, it can be very useful to look at the seasonally adjusted CPI, which removes the effects of seasonal changes, such as weather, school year, production cycles, and holidays.
The CPI can be used to recognize periods of inflation and deflation. Significant increases in the CPI within a short time frame might indicate a period of inflation, and significant decreases in CPI within a short time frame might indicate a period of deflation. However, because the CPI includes volatile food and oil prices, it might not be a reliable measure of inflationary and deflationary periods. For a more accurate detection, the core CPI (CPILFESL) is often used. When using the CPI, please note that it is not applicable to all consumers and should not be used to determine relative living costs. Additionally, the CPI is a statistical measure vulnerable to sampling error since it is based on a sample of prices and not the complete average.
For more information on the CPI, see the Handbook of Methods, the release notes and announcements, and the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs).
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items in U.S. City Average [CPIAUCSL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CPIAUCSL, .
Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
Release: Personal Income and Outlays
Units: Index 2017=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
BEA Account Code: DPCERG
The Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index is a measure of the prices that people living in the United States, or those buying on their behalf, pay for goods and services. The change in the PCE price index is known for capturing inflation (or deflation) across a wide range of consumer expenses and reflecting changes in consumer behavior. For example, if the price of beef rises, shoppers may buy less beef and more chicken.
The PCE Price Index is produced by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), which revises previously published PCE data to reflect updated information or new methodology, providing consistency across decades of data that's valuable for researchers. They also offer the series as a Chain-Type index, as above. The PCE price index is used primarily for macroeconomic analysis and forecasting.
The PCE Price index is the Federal Reserve’s preferred measure of inflation. The PCE Price Index is similar to the Bureau of Labor Statistics' consumer price index for urban consumers. The two indexes, which have their own purposes and uses, are constructed differently, resulting in different inflation rates.
For more information on the PCE price index, see:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Guide to the National Income and Product Accounts of the United States (NIPA)
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Prices & Inflation
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Differences between the Consumer Price Index and the Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Personal Consumption Expenditures: Chain-type Price Index [PCEPI], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PCEPI, .
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Release: Consumer Price Index
Units: Index 1982-1984=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
The "Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food & Energy" is an aggregate of prices paid by urban consumers for a typical basket of goods, excluding food and energy. This measurement, known as "Core CPI," is widely used by economists because food and energy have very volatile prices. The Bureau of Labor Statistics defines and measures the official CPI, and more information can be found in the FAQ or in this article.
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food and Energy in U.S. City Average [CPILFESL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/CPILFESL, .
Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
Release: Personal Income and Outlays
Units: Index 2017=100, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
BEA Account Code: DPCCRG
The Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index is a measure of the prices that people living in the United States, or those buying on their behalf, pay for goods and services. The change in the PCE price index is known for capturing inflation (or deflation) across a wide range of consumer expenses and reflecting changes in consumer behavior. For example, if car prices rise, car sales may decline while bicycle sales increase.
The PCE Price Index is produced by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), which revises previously published PCE data to reflect updated information or new methodology, providing consistency across decades of data that's valuable for researchers. They also offer the series as a Chain-Type index and excluding food and energy products, as above. The PCE price index less food excluding food and energy is used primarily for macroeconomic analysis and forecasting future values of the PCE price index.
The PCE Price Index is similar to the Bureau of Labor Statistics' consumer price index for urban consumers. The two indexes, which have their own purposes and uses, are constructed differently, resulting in different inflation rates.
For more information on the PCE price index, see:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Guide to the National Income and Product Accounts of the United States (NIPA)
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Prices & Inflation
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Differences between the Consumer Price Index and the Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Personal Consumption Expenditures Excluding Food and Energy (Chain-Type Price Index) [PCEPILFE], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PCEPILFE, .
Source: U.S. Federal Open Market Committee
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
Release: Summary of Economic Projections
Units: Percent, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Annual
Notes:
The projections for the federal funds rate are the value of the midpoint of the projected appropriate target range for the federal funds rate or the projected appropriate target level for the federal funds rate at the end of the specified calendar year or over the longer run. Each participant's projections are based on his or her assessment of appropriate monetary policy. The range for each variable in a given year includes all participants' projections, from lowest to highest, for that variable in the given year. This series represents the median value of the range forecast established by the Federal Open Market Committee. For each period, the median is the middle projection when the projections are arranged from lowest to highest. When the number of projections is even, the median is the average of the two middle projections.
Digitized originals of this release can be found at https://fraser.stlouisfed.org/publication/?pid=677.
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Federal Open Market Committee and Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, FOMC Summary of Economic Projections for the Fed Funds Rate, Median [FEDTARMD], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FEDTARMD, .
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: H.15 Selected Interest Rates
Units: Percent, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Monthly
Notes:
Averages of daily figures.
For additional historical federal funds rate data, please see Daily Federal Funds Rate from 1928-1954.
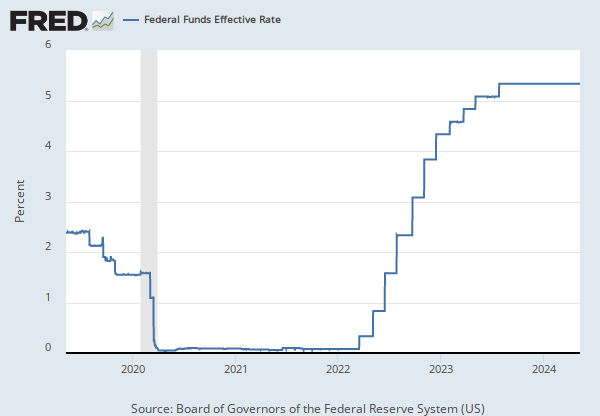
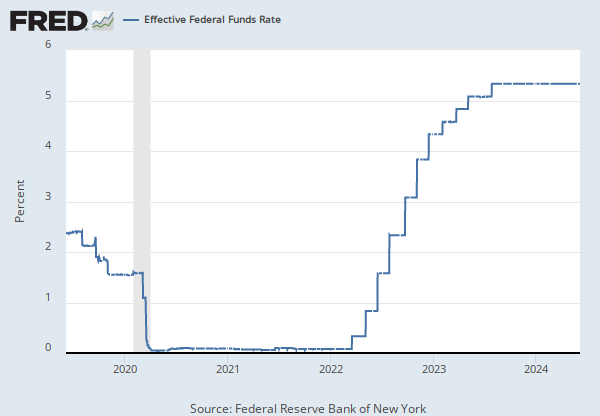
The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions trade federal funds (balances held at Federal Reserve Banks) with each other overnight. When a depository institution has surplus balances in its reserve account, it lends to other banks in need of larger balances. In simpler terms, a bank with excess cash, which is often referred to as liquidity, will lend to another bank that needs to quickly raise liquidity. (1) The rate that the borrowing institution pays to the lending institution is determined between the two banks; the weighted average rate for all of these types of negotiations is called the effective federal funds rate.(2) The effective federal funds rate is essentially determined by the market but is influenced by the Federal Reserve as it uses the Interest on Reserve Balances rate to steer the federal funds rate toward the target range.(2)
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets eight times a year to determine the federal funds target range. The Fed's primary tool for influencing the federal funds rate is the interest the Fed pays on the funds that banks hold as reserve balances at their Federal Reserve Bank, which is the Interest on Reserves Balances (IORB) rate. Because banks are unlikely to lend funds in the federal funds market for less than they get paid in their reserve balance account at the Federal Reserve, the Interest on Reserve Balances (IORB) is an effective tool for guiding the federal funds rate. (3) Whether the Federal Reserve raises or lowers the target range for the federal funds rate depends on the state of the economy. If the FOMC believes the economy is growing too fast and inflation pressures are inconsistent with the dual mandate of the Federal Reserve, the Committee may temper economic activity by raising the target range for federal funds rate, and increasing the IORB rate to steer the federal funds rate into the target range. In the opposing scenario, the FOMC may spur greater economic activity by lowering the target range for federal funds rate, and decreasing the IORB rate to steer the federal funds rate into the target range. (3) Therefore, the FOMC must observe the current state of the economy to determine the best course of monetary policy that will maximize economic growth while adhering to the dual mandate set forth by Congress. In making its monetary policy decisions, the FOMC considers a wealth of economic data, such as: trends in prices and wages, employment, consumer spending and income, business investments, and foreign exchange markets.
The federal funds rate is the central interest rate in the U.S. financial market. It influences other interest rates such as the prime rate, which is the rate banks charge their customers with higher credit ratings. Additionally, the federal funds rate indirectly influences longer- term interest rates such as mortgages, loans, and savings, all of which are very important to consumer wealth and confidence.(2)
References
(1) Federal Reserve Bank of New York. "Federal funds." Fedpoints, August 2007.
(2) Monetary Policy, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
(3) The Fed Explained, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
For further information, see The Fed's New Monetary Policy Tools, Page One Economics, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
For questions on the data, please contact the data source. For questions on FRED functionality, please contact us here.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Federal Funds Effective Rate [FEDFUNDS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FEDFUNDS, .
Release Tables
- CPI for U.S. City Average: Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted
- CPI for U.S. City Average: Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items in U.S. City Average
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Semiannual, Not Seasonally AdjustedPersonal Consumption Expenditures: Chain-type Price Index
Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Quarterly, Seasonally AdjustedConsumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items Less Food and Energy in U.S. City Average
Monthly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Semiannual, Not Seasonally AdjustedPersonal Consumption Expenditures Excluding Food and Energy (Chain-Type Price Index)
Percent Change from Quarter One Year Ago, Quarterly, Seasonally AdjustedFederal Funds Effective Rate
Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Biweekly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Daily, Not Seasonally Adjusted Daily, Not Seasonally Adjusted Weekly, Not Seasonally AdjustedRelated Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.